
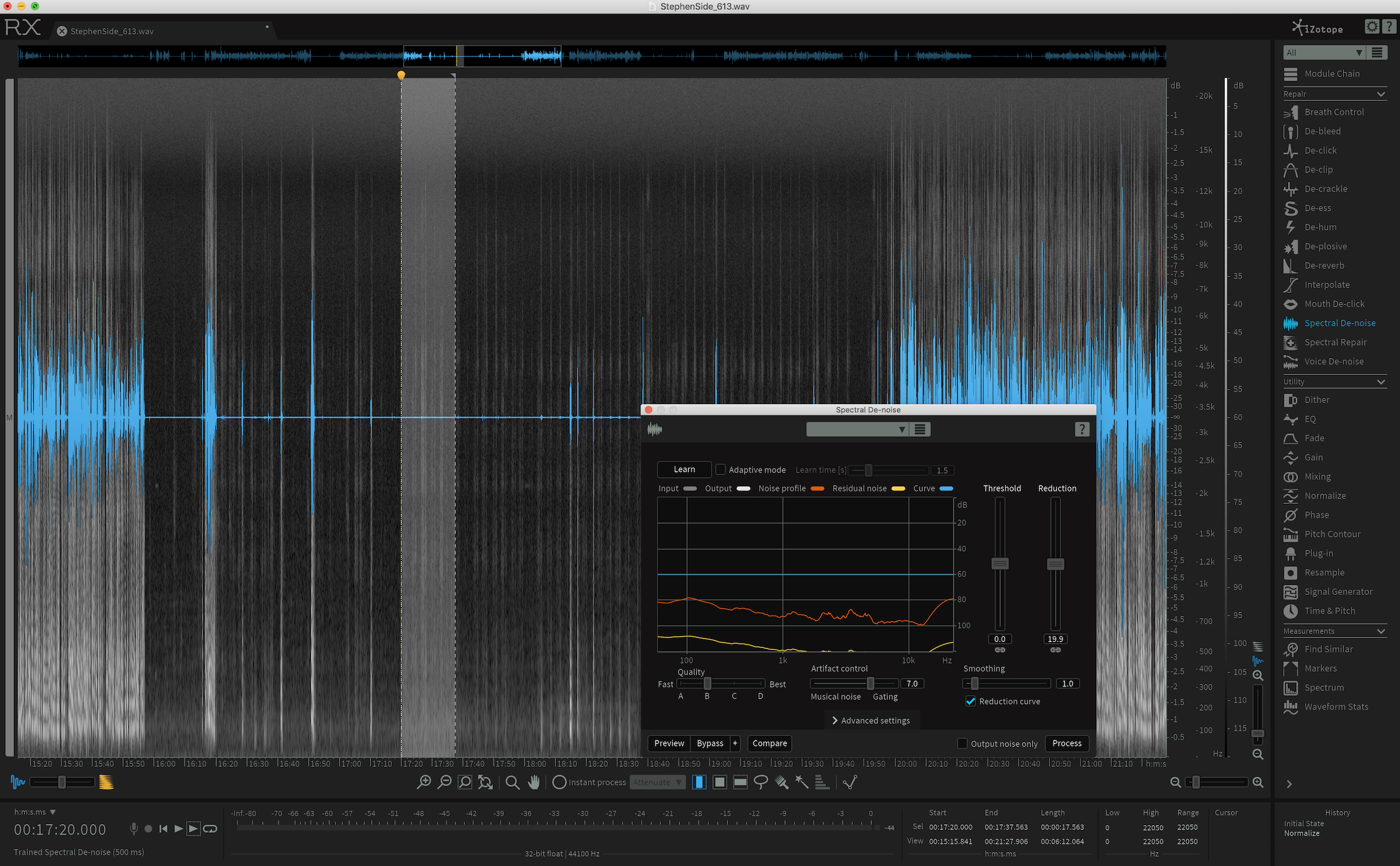
#Spectral denoise verification#
If this occurs, set the detection threshold rather low, and select Second Level Verification to reanalyze the detected clicks and disregard percussive transients that aren’t clicks.Īls een regio wordt geselecteerd, wordt de taal en/of de content gewijzigd op Cleanup - Noise Reduction There are two ways of reducing noise. With too much distortion of this type, audio begins to sound flat and lifeless. If more clicks are detected, more repair occurs, increasing the possibility of distortion. The level can be as low as 6, but a lower setting can cause the filter to remove sound other than clicks. If a constant crackle is in the background of the source audio, try lowering the Min Threshold level or increasing the dB level to which the threshold is assigned. These settings allow for the most clicks to be found, and usually all of the louder ones. Start with a threshold of 35 for high-amplitude audio (above -15 dB), 25 for average amplitudes, and 10 for low-amplitude audio (below-50 dB). Possible values range from 1 to 150, but recommended values range from 6 to 60. Clicks are very noticeable in very quiet audio, so quiet audio tends to require lower detection and rejection thresholds.ĭetermines sensitivity to clicks and pops. In general, less correction is required for louder audio, as the audio itself masks many clicks, so repairing them isn’t necessary. If a loud piece still has clicks, lower the Average or Maximum Threshold level. For example, if a quiet part still has a lot of clicks, lower the Minimum Threshold level a bit. For example, if Maximum Threshold is set to 30 and Minimum Threshold is set to 10, set Average Threshold to 25.Īfter you audition a small piece of repaired audio, you can adjust the settings as needed.
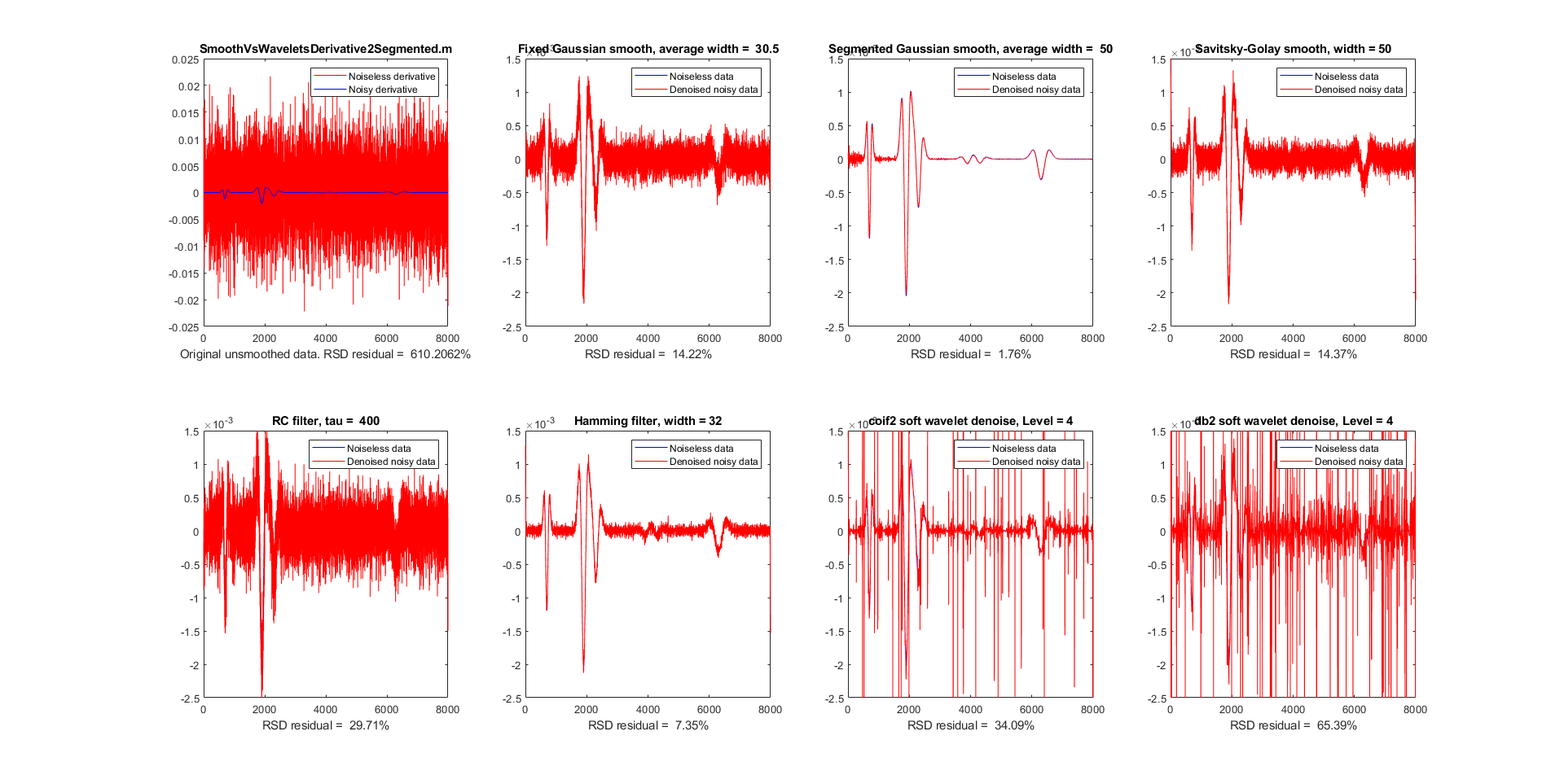
(Set the Maximum and Minimum Threshold levels first, because once they’re in place, you shouldn’t need to adjust them much.) Set the Average Threshold level to about three quarters of the way between the Maximum and Minimum Threshold levels.

Set the threshold levels before you adjust the corresponding Detect and Reject values. If the minimum RMS amplitude is -55 dB, then set Minimum Threshold to -55. For example, if audio has a maximum RMS amplitude of -10 dB, you should set Maximum Threshold to -10 dB.
#Spectral denoise how to#
How to match, fade, and mix clip volume with Audition.Arrange and edit multitrack clips with Audition.How to use special effects with Audition.Diagnostics effects (Waveform Editor only) for Audition.Apply amplitude and compression effects to audio.Doppler Shifter effect (Waveform Editor only).
#Spectral denoise manual#
Manual Pitch Correction effect (Waveform Editor only).Fade and Gain Envelope effects (Waveform Editor only).Applying effects in the Waveform Editor.Analyze phase, frequency, and amplitude with Audition.How to automate common tasks in Audition.Inverting, reversing, and silencing audio.How to copy, cut, paste, and delete audio in Audition.Displaying audio in the Waveform Editor.Matching loudness across multiple audio files.Edit, repair, and improve audio using Essential Sound panel.Remove silences from your audio recordings.Monitoring recording and playback levels.Navigate time and playing audio in Adobe Audition.Create, open, or import files in Adobe Audition.Customizing and saving application settings.Connecting to audio hardware in Audition.Applying effects in the Multitrack Editor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
